|
In Information Security, intrusion detection is the act of detecting actions that attempt to compromise the confidentiality, integrity or availability of a resource. When Intrusion detection takes a preventive measure without direct human intervention, then it becomes an Intrusion-prevention system. Intrusion detection can be performed manually or automatically. Manual intrusion detection might take place by examining log files or other evidence for signs of intrusions, including network traffic. A system that performs automated intrusion detection is called an Intrusion Detection System (IDS). An IDS can be either host-based, if it monitors system calls or logs, or network-based if it monitors the flow of network packets. Modern IDSs are usually a combination of these two approaches. Another important distinction is between systems that identify patterns of traffic or application data presumed to be malicious (misuse detection systems), and systems that compare activities against a ’normal’ baseline (anomaly detection systems). When a probable intrusion is discovered by an IDS, typical actions to perform would be logging relevant information to a file or database, generating an email alert, or generating a message to a pager or mobile phone. Determining what the probable intrusion actually is and taking some form of action to stop it or prevent it from happening again are usually outside the scope of intrusion detection. However, some forms of automatic reaction can be implemented through the interaction of Intrusion Detection Systems and access control systems such as firewalls. Some authors classify the identification of attack attempts at the source system as extrusion detection (also known as outbound intrusion detection) techniques. Intrusion prevention is an evolution of intrusion detection. Information security means protecting information and information systems from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, perusal, inspection, recording or destruction. The terms information security, computer security and information assurance are frequently incorrectly used interchangeably. These fields are interrelated often and share the common goals of protecting the confidentiality, integrity and availability of information; however, there are some subtle differences between them. These differences lie primarily in the approach to the subject, the methodologies used, and the areas of concentration. Information security is concerned with the confidentiality, integrity and availability of data regardless of the form the data may take: electronic, print, or other forms. Computer security can focus on ensuring the availability and correct operation of a computer system without concern for the information stored or processed by the computer. Governments, military, corporations, financial institutions, hospitals, and private businesses amass a great deal of confidential information about their employees, customers, products, research, and financial status. Most of this information is now collected, processed and stored on electronic computers and transmitted across networks to other computers. Should confidential information about a business’ customers or finances or new product line fall into the hands of a competitor, such a breach of security could lead to lost business, law suits or even bankruptcy of the business. Protecting confidential information is a business requirement, and in many cases also an ethical and legal requirement. For the individual, information security has a significant effect on privacy, which is viewed very differently in different cultures. The field of information security has grown and evolved significantly in recent years. There are many ways of gaining entry into the field as a career. It offers many areas for specialization including: securing network(s) and allied infrastructure, securing applications and databases, security testing, information systems auditing, business continuity planning and digital forensics science, etc. This article presents a general overview of information security and its core concepts 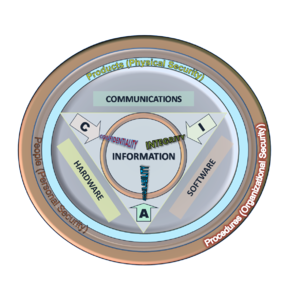
Information Security Components: or qualities, i.e., Confidentiality, Integrity and Availability (CIA). Information Systems are decomposed in three main portions, hardware, software and communications with the purpose to identify and apply information security industry standards, as mechanisms of protection and prevention, at three levels or layers: Physical, personal and organizational. Essentially, procedures or policies are implemented to tell people (administrators, users and operators)how to use products to ensure information security within the organizations. In general, detection is the extraction of particular information from a larger stream of information without specific cooperation from or synchronization with the sender. In the history of radio communications, the term "detector" was first used for a device that detected the simple presence or absence of a radio signal, since all communications were in Morse code. The term is still in use today to describe a component that extracts a particular signal from all of the electromagnetic waves present. Detection is usually based on the frequency of the carrier wave, as in the familiar frequencies of radio broadcasting, but it may also involve filtering a faint signal from noise, as in radio astronomy, or reconstructing a hidden signal, as in steganography. In optoelectronics, "detection" means converting a received optical input to a electrical output. For example, the light signal received through an optical fiber is converted to an electrical signal in a detector such as a photodiode. In steganography, attempts to detect hidden signals in suspected carrier material is referred to as steganalysis. Steganalysis has an interesting difference from most other types of detection, in that it can often only determine the probability that a hidden message exists; this is in contrast to the detection of signals which are simply encrypted, as the ciphertext can often be identified with certainty, even if it cannot be decoded. In the military, detection refers to the special discipline of reconnaissance with the aim to recognize the presence of an object in a location or ambiance. Finally, the art of detection, also known as following clues, is the work of a detective in attempting to reconstruct a sequence of events by identifying the relevant information in a situation.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia : Security and detection |


